When Kimi K2 Meets vLLM: A Deep Dive from Crashing to Fixing Tool Calls
A debugging session on the performance collapse of Kimi K2 model's tool calls on vLLM, revealing easily overlooked engineering details behind LLM APIs. The issue isn't the model's capability but the subtleties of prompt construction and output parsing.
Moonshot AI's Kimi K2 model is renowned for its exceptional tool calling abilities. However, on the high-performance inference engine vLLM, its performance was a shock: near-perfect tool calls on the official API achieved success rates of less than 20% on vLLM.
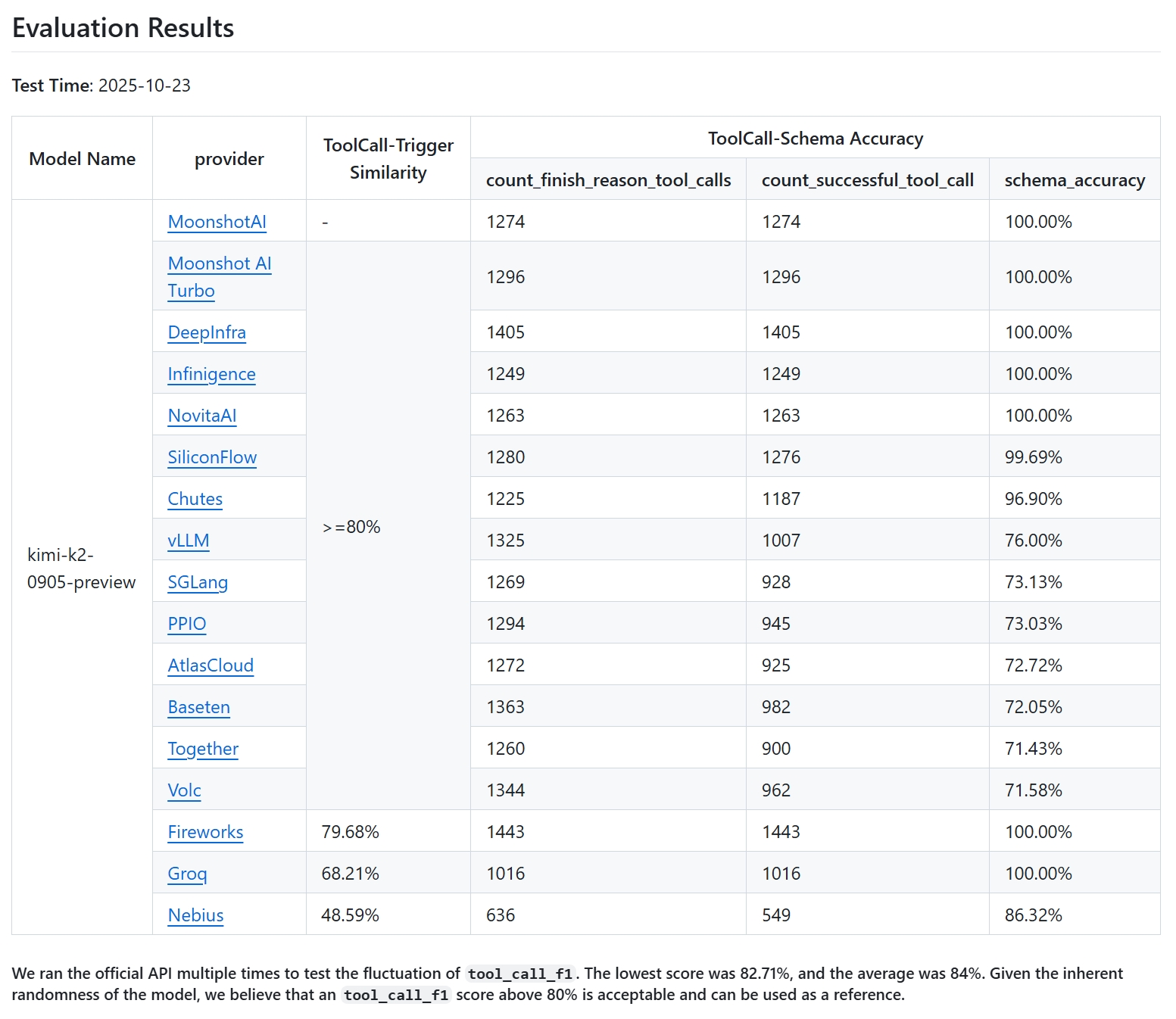
This table vividly illustrates the severity of the issue. On the official API, the model could execute thousands of tool calls with zero schema validation errors; in initial vLLM tests, only 218 successful tool call parses were achieved.
## The Problem Isn't the Model, But the Pipeline
The core discovery is that tool call failures weren't due to the 'model not knowing how to use tools,' but rather compatibility issues in prompt rendering and output parsing.
The essence of modern LLM APIs can be simplified into three steps: rendering (constructing the final prompt), completion (model generation), and parsing (structuring the output). Advanced features like tool calls are merely engineering wrappers added on this basic pipeline.
## Three Specific Issues and Their Fixes
### 1. Missing Generation Prompt
The most critical issue was that vLLM didn't pass the `add_generation_prompt=True` parameter. This caused the prompt to lack the essential 'it's the assistant's turn to respond' marker, leaving the model unsure whether to generate a tool call or regular text next.
**Fix:** The Kimi team updated the tokenizer configuration to explicitly declare this parameter.
### 2. Incorrect Rendering of Empty Content
When the `content` field in historical messages was an empty string, vLLM would convert it to a complex structure `[{'type': 'text', 'text': ''}]`, which Kimi's template couldn't handle correctly, leading to prompt pollution.
**Fix:** Modified the chat template to add logic for judging content types.
### 3. Too Strict Parser
Even if the model generated a usable tool call, vLLM's parser would discard the entire result due to slight deviations in ID format. For example, the model generated `search:2`, while the official API required `functions.search:2`.
**Fix:** Suggested users normalize historical tool call ID formats before sending requests.
## The Value of Debugging Methodologies
The most effective method during this debugging process was bypassing the advanced API and manually constructing the flow:
1. Externally call `apply_chat_template` to obtain the complete prompt
2. Send the prompt to the lower-level `/completions` endpoint
This approach allows one to directly see the model's actual input and raw output, avoiding problems obscured by abstraction layers.
## Post-Fix Performance and Limitations
After the fix, successful tool call parses increased from 218 to 971—a 4.4x growth. However, schema validation errors still existed compared to the official API.
The key difference lies in the official API's 'executor' component, which ensures the model only generates tokens corresponding to the tools provided in the current request through constrained decoding. This represents a significant gap between open-source ecosystems and mature commercial services.
## Insights for Developers
- **Chat templates are devil details:** In model-inference framework integration, template logic is the最容易出错环节
- **Lower abstraction levels:** When troubleshooting, checking raw prompts and completion texts often quickly identifies the cause
- **Understand framework design philosophy:** vLLM's strict parameter passing restrictions are security considerations, not bugs
This debugging session not only resolved specific technical issues but also provided a window into understanding the underlying logic of LLM services. Tool calling capabilities depend not just on the model, but on the fine-tuning of the entire service pipeline.
发布时间: 2025-12-25 17:26